
VARIOUS SPECIALISATIONS AT A GLANCE
Oncology/Oncologist
An oncologist specializes in diagnosing and treating cancer “using chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, biological therapy, and targeted therapy. Often, he is the main healthcare provider for cancer patients. The three main types of oncologists are medical, surgical, and radiation oncologists. A person suffering from cancer or tumor is often treated by a multidisciplinary team of oncologists, who specialize in different areas. Other medical professionals involved in a patient's care are Pathologist, Diagnostic radiologist, dermatologist, etc.
A medical oncologist treats cancer using chemotherapy (the use of drugs to kill cancer cells). A surgical oncologist specializes in the surgical aspects of cancer, including a biopsy (the removal of a small amount of tissue for examination under a microscope) and surgically removing cancer, the surrounding tissue, and sometimes, nearby lymph nodes (tiny, bean-shaped organs that help fight disease). A radiation oncologist specializes in treating cancer with radiation therapy.
Some other types of oncologists are a gynecologic oncologist who deals with gynecologic cancers, such as uterine cancer and cervical cancer. A pediatric oncologist specializes in the treatment of children with cancer.
Personal skills: You need to be sensitive to handle the patient with love and care. Must possess good interpersonal skills, and in particular be a good listener, Be self-motivated to be able to put in hard work. Aptitude to keep abreast with the latest developments is also needed.
Pay & Perks: In the government sector, a surgical/medical oncologist can easily earn Rs.50,000 to 80,0000 a month, As one gains experience, he could earn 90,000 to Rs.1, lakh or above per month. Pay package varies in the private sector, depending upon the level and standard or the establishment vis-a-vis your knowledge, expertise, and reputation in the profession.
How to enter?
To be an oncologist, after completing high school, you need to study science with Physics, Chemistry, and Biology. Complete your MBBS, after which you can do either of these three-year courses: (a) MS, followed by a three-year M.ch programme, b) MD (Medicine/pediatrics), topped up with a DM (medical oncology) qualification or C) MD in radiotherapy. If you can't do Ms or MD, opt for DNB (Diploma).
Surgery
General Surgeon
A general surgeon deals with common problems that occur in the abdomen, digestive tract, endocrine system, breast, skin, and blood vessels. Common problems treated by general surgeons include hernias, breast tumors, gallstones, appendicitis, pancreatitis, bowel obstructions, colon inflammation, and colon cancer. He/ she diagnoses the problems and treat the patient with the use of minimally invasive and endoscopic ( looking inside and typically refers to looking inside the body for medical reasons using an endoscope, an instrument used to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body) techniques.
A general surgeon is also trained in the care of pediatric and cancer patients and in the treatment of patients who are injured or critically ill. He generally receives training in hand surgery, hospice and palliative medicine, pediatric surgery, surgical critical care, vascular surgery.
Skills required: Ability to work well under stress and pressure, team spirit, thorough knowledge of the human body and related surgical procedures, fine motor skills to perform intricate surgical specialties such as neurosurgery, commitment, determination, and competitive spirit are important personal attributes required to be a successful surgeon.
Colon and Rectal Surgeon OR Colorectal Surgeons
Colorectal surgery deals with disorders of the rectum, anus, and colon. Physicians specializing in this field are colorectal surgeons or proctologists.
What do they do?
A colon and rectal surgeon is trained medical professional who has expertise in diagnosing and treating various diseases of the small intestine, colon, rectum, anal canal, and per anal area by medical and surgical means. These specialists also deal with other organs and tissues (such as the liver, urinary and female reproductive system) involved with the primary intestinal disease.
Orthopedic Surgeon
Orthopedics is a surgical discipline that employs many tools to insert equipment such as pins, rods, and bolts.
An orthopedic surgeon has expertise in the preservation, investigation, and restoration of the form and function of the extremities, spine, and associated structures by medical, surgical, and physical means. He/she is involved with the care of patients whose musculoskeletal problems include congenital deformities, trauma, infections, tumors, metabolic disturbances of the musculoskeletal system, deformities, injuries, and degenerative diseases of the spine, hands, feet, knee, hip, shoulder, and elbow in children and adults. An orthopedic surgeon is also concerned with primary and secondary muscular problems and the effects of the central or peripheral nervous system lesions of the musculoskeletal system.
Orthopedic surgeons can receive training in orthopedic sports medicine, Surgery of the hand.
Skills required: Specific surgical skills including methods of preventing infector’s through techniques such as washing hands, using sterile linens and supplies, positioning and using the various protective equipment. They need to learn to make an incision and master the various steps involved in tying surgical knots.
Moreover, they must be able to use multiple approaches to solve problems associated with typical injuries. It requires critical thinking, a spirit to serve and help patients, as well as problem solving ability by applying scientific methods, good communication skills and team spirit, is also required.
Plastic Surgeon
A plastic surgeon deals with the repair, reconstruction, or replacement of physical defects of form or function. These could be of the skin, musculoskeletal system, head and facial structures, hands, extremities, breasts, and trunk or cosmetic enhancement of these areas. Cosmetic surgery is a part of plastic surgery. A plastic surgeon uses reconstructive procedures applying cosmetic surgical principles to improve overall appearance.
Neurology/Neurologist
A neurologist deals with diagnosis and treatment of diseases pertaining to the brain or impaired function of the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, muscles, and autonomic nervous system as well as the blood vessels that relate to these structures.
To be a successful neurologist, you need to specialise in clinical neurophysiology, specialization in the diagnosis and management of central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous system disorders using a combination of clinical evaluation and electrophysiological testing such as electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG), and nerve conduction studies (NCS), among others. Neurologists work intricately with psychiatrists and general practitioners to alleviate the condition of their specific patients. As such, they require precision and communication skills, as well as an ability to think outside a given pattern and come up with sometimes unprecedented solutions.
Skills required: by neurologists are diagnostic skills, communication skills, research skills, memory skills.
Obstetrician/Gynecologist
Obstetrics and gynecology is concerned with the care of the pregnant woman, her unborn child and the management of diseases specific to women. An obstetrician/gynecologist possesses special knowledge, skills, and professional capability in the medical and surgical care of the female reproductive system and associated disorders. He/she serves as a consultant to other physicians and as a primary physician for women. Obstetrics and gynecology is an exciting area. Many new techniques and procedures have been developed over the past 30 years and transformed the health of women and babies. It is an evolving discipline with many research arms, both at clinical and molecular level.
Obstetrician/gynecologists generally receive training in the following subspecialties: critical care medicine, gynecologic oncology, hospice, and palliative medicine, maternal and fetal medicine, reproductive endocrinology and infertility
Skills required: Active listening skills are necessary to fully understand the symptoms, ailments, and concerns of patients. Obstetricians and gynecologists must be highly sensitive to the needs of patients and have significant critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Obstetricians and gynecologists are very service oriented, meaning they are genuinely interested in helping people. They also possess inductive and deductive reasoning skills to properly analyze patient information even if the patient does not provide the entire story.
Pathology/Pathologists
A pathologist deals with the causes and nature of diseases and contributes to diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment through knowledge gained by the laboratory application of the biologic, chemical, and physical sciences. He uses information gathered from the microscopic examination of tissue specimens, cells, and body fluids, and from clinical laboratory tests on body fluids and secretions for the diagnosis, exclusion, and monitoring of disease.
A pathologist receives training in Blood banking/transfusion medicine, Chemical pathology, Cytopathology, Dermatopathology, Forensic pathology, Hematology, Medical Microbiology, Molecular genetics pathology, Neuropathology, and Pediatric pathology.
Skills required: Accuracy, analytical and interpretation ability, good communication ability particularly in writing reports, and to work under pressure.
Neurological Surgeon
A surgeon who deals with prevention, diagnosis, evaluation, treatment, critical care, and rehabilitation of disorders of the central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems, including their supporting structures and vascular supply is called the Neurological surgeon. He is trained in the subspecialty like endovascular surgical neuroradiology, radiologic imaging, and clinical expertise.
Thoracic surgeon
Operations on the heart, lungs, esophagus, and other organs in the chest are performed by a Thoracic surgeon. Types of thoracic surgeons include cardiothoracic surgeons, cardiovascular surgeons, general thoracic surgeons, and congenital heart surgeons.
Thoracic surgeons are trained in congenital cardiac surgery, which involves operative treatment of structural abnormalities involving the heart and major blood vessels.
Skills required: Active listening, critical thinking, complex problem solving, judgment and decision making.
Anesthesiologist
An anesthesiologist is a medical professional who has expertise in providing pain relief and maintenance or restoration of a stable condition of the patient during and immediately after an operation or diagnostic procedure. He/she diagnoses and treats acute, long-standing, and cancer pain problems as well as critical illnesses; and severe injuries.
Anesthesiologist receives training in:
Critical care medicine (supporting critically ill and injured patients, particularly trauma victims and patients with multiple organ dysfunction, etc.); hospice and palliative medicine, pain medicine, etc.
Skills required: Communication and interpersonal skills, ability to explain complex technical issues, decision-making, and integration skills
Dermatologist
A dermatologist is a skin specialist. He/she diagnose and treat pediatric and adult patients with disorders of the skin, mouth, external genitalia, hair, and nails as well as a number of sexually transmitted diseases (STD). Dermatologist receives training in the subspecialties like dermatopathology, pediatric dermatology, procedural dermatology, etc.
Skills required: A dermatologist needs an excellent understanding of the skin and subcutaneous tissue anatomy, cetaceous microanatomy and biology, clinical pharmacology, basic immunology, and basic radiation physics and radiobiology, Ability to perform procedures including biopsies, cryotherapy and the removal of skin lesions. Good interpersonal and communicative skills coupled with empathy to counsel patients suffering from psychological stress.
Ophthalmologist
An ophthalmologist is a specialist who deals with medical and surgical eye problems. He takes care of the eye and vision care for patients of all ages. He diagnoses, monitors, and medically or surgically treats all ocular and visual disorders. To provide consultative services for the diagnosis and management of ocular manifestation of systemic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and infectious and non-infectious inflammation is also a part of his duty.
To be a successful ophthalmologist, you must have strong physics and math skills as well as a good medical knowledge. Good manual skills to use instrument are indispensable. Must have good vision. Good patient communication skills and the ability to work as part of a team since ophthalmologists work closely with optometrists, orthoptists, nurses, nurse practitioners, and managers.
Otolaryngology
An otolaryngologist is a head and neck surgeon. He deals with disorders of ears, nose, throat, the respiratory and upper alimentary systems, and related structures. He/she diagnoses and provides medical and surgical therapy or prevention of allergies, deformities, disorders, and injuries.
Otolaryngologists can receive subspecialties in neurotology, pediatric otolaryngology, plastic surgery, reconstructive procedures within the head, face, neck, and associated structures, including cutaneous head and neck oncology and reconstruction, management of maxillofacial trauma, soft tissue repair, and neural surgery.
Pediatrician
A pediatrician is a specialized medical professional to diagnose and treat different types of chronic disorders, injuries, and infections in infants, children, and teens. He/she performs general check-ups, offers vaccination or immunization therapies to the newborn babies, treats certain diseases such as sinus infections, ear infections, sore throats, mononucleosis, and flu to name a few. In addition, the pediatricians prescribe an appropriate medication and provide emergency child care including follow-up care.
Pediatricians are generally trained in the subspecialties like neonatal- perinatal medicine, pediatric critical care medicine, pediatric emergency medicine, pediatric gastroenterology, pediatric cardiology, pediatric endocrinology, pediatric sports medicine, etc.
Skills required: Strong knowledge of biology, psychology, anatomy, physiology and the principles of counseling and therapy. Good communication skill including active listening. Ability to perform in medical procedures and conducting physical examinations is absolutely necessary. Good computer skills make it possible to use electronic medical records systems and other technology.
Psychiatrist
A psychiatrist is a physician who specializes in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of mental, addictive, and emotional disorders such as schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders, mood disorders, anxiety disorders, sexual and gender identity disorders, etc.
His job is to understand the biologic, psychological, and social components of illness in order to uniquely treat the whole person. A psychiatrist is qualified to order diagnostic laboratory tests and to prescribe medications, evaluate, and treat psychological and interpersonal problems. He also intervenes with families who are coping with stress, crises, and other problems in living.
Psychiatrists are trained in the subspecialties such as addiction psychiatry, child and adolescent psychiatry, clinical neurophysiology, forensic psychiatry, geriatric psychiatry hospice and palliative medicine, pain management, psychosomatic medicine, etc.
To be a successful psychiatrist besides adequate professional training, one needs qualities of head and heart- sympathy and love for the suffering people, patience to listen and understand effective communication skills.
Radiologist
A radiologist uses imaging methodologies such as x-ray, ionizing radiation, radionuclide, electromagnetic radiation, ultrasound, and image-guided intervention to diagnose patients.
Radiologists are trained in the following subspecialties: neuroradiology, nuclear radiology, pediatric radiology, vascular and interventional radiology.
Skills required: Comprehensive understanding of the human anatomy and medical and scientific principles relating to human health. Should be technically savvy. Must have excellent vision and analytical skills.
Urologist
Urology is the study of the anatomy, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of genitourinary disorders. A urologist manages congenital and acquired conditions of the genitourinary system and contiguous structures including the adrenal gland. The urologist is skilled in medical and open surgical therapy of these conditions as well as endoscopic, percutaneous, and other minimally invasive methods.
Urologists often specialize within urology, for example, focusing on men's urology, oncology, laparoscopic (minimally invasive) surgery, pediatric urology, or other areas. For example, if you have a child with a urologic problem, you will want to find a urologist whose practice focuses exclusively on pediatric urology.
Audiologist
An audiologist identifies, diagnoses, treats and monitors disorders of the auditory and vestibular system portions of the ear.
Skills required: To work in audiology you will need effective communication with an excellent problem-solving ability along with team skills. Confidence in using technology and systems/processes.
Hematologist
The core job of a Hematologist is to provide an advisory and consultancy service to all hospital specialists and general practitioners and manage diagnostic laboratories. He provides clinical interpretation of laboratory data and morphology of blood and bone marrow specimens. In addition, delivering clinical care, often for life-threatening disease, formulating chemotherapy protocols and managing their delivery; managing hemopoietic stem cell transplantation procedures; providing advice on hematology laboratory results; sampling bone marrow and interpreting the morphology, etc. are some other jobs of a hematologist.
Hematologists generally go for specialties in haemato-oncology, homeostasis /thrombosis, disorders of blood production and destruction (including bone marrow failure, anemia and autoimmune blood diseases), transfusion medicine and pediatric hematology.
Histopathologist / Histopathology
Histopathology is the diagnosis and study of disease by expert medical interpretation of cells and tissue samples. The specialty determines the cause of death by performing autopsies and is integral to cancer management through staging and grading of tumors. Histopathologist works in the lab with laboratory scientists and doctors from other clinical specialties. He has in-depth knowledge of both pathological and clinical aspects of the disease. His functions are to examine and dissect surgical resection specimens, to select the most appropriate samples for microscope slides, to observe and note down microscopic examination of tissues to prepare clinical reports.
Microbiologists and Virologists
Medical microbiologists and virologists are the specialists who diagnose, treat and help in the prevention of the spread of infection in the community.
The job of microbiologist is to provide advice on the likely causes and suggest the best tests to diagnose it. Tests may involve the identification of parasites under the microscopy, the use of biochemical tests to identify colonies of bacteria or the use of molecular tests to identify organisms (or even specific genes) which may govern an organism’s behavior.
A microbiologist supervises the running of the diagnostic laboratory, and ensures the delivery of prompt and accurate test results to patients.
Microbiologist works with hospital infection control teams to reduce the spread of infections in hospitals. He contributes to the protection of public health by monitoring the patterns of infectious diseases and reporting new or unusual occurrences of infections. In their infection control activities, microbiologists have to work with nurses and other healthcare professionals, hospital estates departments and management.
Skills required: Proficiency with the precision instrument; ability to identify microbes and recognize significant discoveries; meticulous observance and practice of safety procedures; research and communication skills, etc.
Plastic surgeon
Plastic surgeon shapes and molds regions of the body, such as the ears, face, trunk, hands and other extremities for cosmetic and functional effect. He repairs congenital problems, such as a malformed bone structure in hands or feet. He performs many types of reconstructive surgery. The surgeries that a plastic surgeon performs include hand surgery, microsurgery, and the treatment of bums. Cosmetic surgery reshapes normal body parts for aesthetic reasons, while reconstructive surgery repairs or replaces body parts damaged by accidents, illness or malformation.
Skills Required: Plastic surgeons must be driven, focused individuals who are able to sustain many years of schooling and long work hours. They are licensed medical doctors trained in patient interactions, trauma care and basic surgery techniques, as well as specialized areas, such as tissue transfer, body contouring and laser surgery.
Rheumatologist
The role of the rheumatologist is to diagnose, treat and advise patients with arthritis and problems affecting the joints, muscles, bones and sometimes other internal organs (e.g., kidneys, lungs, blood vessels, and brain).
A rheumatologist needs good general medical knowledge and proficiency in rheumatic medicine to be interested in helping people with disorders of the joints and all rheumatic diseases; to enjoy finding solutions to problems; a broad and empathetic approach as often the conditions have psychosocial ramifications; excellent communication skills to liaise with other physicians and provide clear information to patients; stamina to work long hours; emotional strength and maturity and strong ethics.
Internal Medicine
Internal medicine or general medicine is the medical specialty dealing with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of adult diseases. Physicians specializing in internal medicine are called internists. He provides long-term comprehensive care in the office and the hospital, managing both common and complex illness of adolescents, adults, and the elderly.
Internists are trained in the diagnosis and treatment of of cancer, infections, and diseases affecting the heart, blood, kidneys, joints and digestive, respiratory, and vascular systems. They are also trained in the essentials of primary care internal medicine which incorporates an understanding of disease prevention, wellness, substance abuse, mental health, and effective treatment of common problems of the eyes, ears, skin, nervous system, and reproductive organs.
Internists can receive training in the subspecialties like adolescent medicine, cardiovascular disease, clinical cardiac electrophysiology, endocrinology, diabetes & metabolism, critical care medicine, gastroenterology geriatric medicine, hematology, hospice and palliative medicine infectious disease, interventional cardiology, medical oncology, nephrology, pulmonary disease, etc.
Nuclear Medicine Specialist
A nuclear medicine specialist uses the tracer principle to evaluate molecular, metabolic, physiologic and pathologic conditions of the body for the purposes of diagnosis, therapy and research. Nuclear medicine encompasses molecular imaging. Imaging systems are used to detect the tracer signal to provide spatial and temporal information on the processes of interest.
The nuclear medicine physician often uses anatomic imaging combined with molecular imaging (e.g., PET/CT). The most common diagnostic applications of nuclear medicine include the early detection of coronary artery disease, cancer diagnosis and staging, and the evaluation of the effect of cancer treatment. Some types of radioactive molecules can be used to treat cancer (e.g., lymphoma, thyroid cancer) or relieve the severe pain caused by cancer that has spread to the bone.
Diplomate of National Board
Diplomate of National Board (DNB) is the title awarded by the National Board of Examinations (NBE), an autonomous academic body under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India to candidates who successfully complete their postgraduate or postdoctoral medical education under it.
The Board conducts its postgraduate and postdoctoral programmes in teaching hospitals accredited by it and in medical colleges accredited by the Medical Council of India.
The degrees are recognized by the Government of India and a Gazette order is published for the same. Also, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has issued notification mentioning that DNB should always be considered equivalent to MD.
Since 2009, the DNB qualifications awarded by the National Board of Examinations have been equated with postgraduate and postdoctoral qualifications awarded by other Indian universities for all purposes, including appointment to teaching posts.
Three-year postgraduate residency programme is available in the following broad specialties:
- Anatomy, 2. Physiology, 3. Biochemistry, 4. Pathology, 5. Microbiology, 6. Forensic Medicine, 7. Pharmacology, 8. General Medicine, 9. Pediatrics, 10. Psychiatry, 11. Radio Therapy, 12. Radio Diagnosis, 13. Anesthesiology, 14. Dermatology & Venereology, 15. Respiratory Diseases, 16. Nuclear Medicine, 17. General Surgery, 18. Orthopedic Surgery, 19. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 20. Ophthalmology, 21. Otorhinolaryngology, 22. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 23. Social and Preventive Medicine, 24. Health Administration (including Hospital Administration), 25. Family Medicine, 26 Immunohematology & Transfusion Medicine, 27. Maternal and Child Health, 28. Rural
Super specialties for DNB
Three-year residency programme is available in the following super specialties:
- Cardiology
- Gastroenterology
- Nephrology
- Endocrinology
- Neurology
- Medical Oncology
- Hematology
- Rheumatology
- Cardio Thoracic Surgery
- Pediatric Surgery
- Genito Urinary Surgery (Urology)
- Neurosurgery
- Plastic Surgery
- Surgical Gastroenterology
- Surgical Oncology
- Peripheral Vascular Surgery
Subspecialties for FNB:
The National Board of Examinations also runs postdoctoral fellowship programme in select subspecialties. On successful completion of two-year residency, candidates are awarded Fellow of National Board (FNB).
Fellowship programme is available in the following subspecialties:
- Critical Care Medicine
- Reproductive Medicine
- Cardiac Anesthesia
- Minimal Access Surgery
- Vitreo-Retinal Surgery
- Interventional Cardiology
- Pediatric Cardiology
- Spine Surgery
- Hand & Micro Surgery
- Trauma Care
- Pediatrics Hemato Oncology
- Pediatric Intensive Care
- Laboratory Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- High Risk Pregnancy & Perinatology.
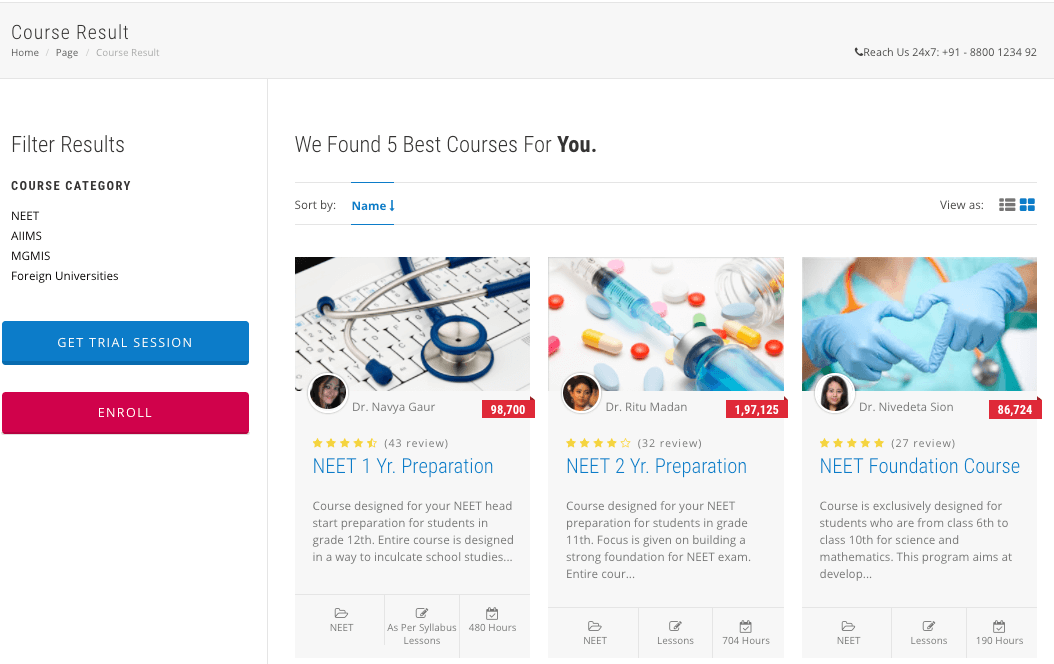
NEET Coaching Program
NEET 1 Yr. Course | View Course Details
NEET 2 Yr. Course | View Course Details
NEET Foundation Course | View Course Details
NEET Online Test Series | View Course Details
NEET Course Features Designed
1. Live and Online NEET Classes – All NEET preparation classes are live and interactive, means we do not provide any recordings. We do it real time on our whiteboard with inbuilt voice and camera feature. Such classes help you to interact with faculty in real time and enable discussion over the topic which is a necessity for NEET preparation. We do not entertain Skype calls etc. for NEET preparation classes. Our online whiteboard is integrated with camera and mic functionality to keep you at ease and make things formal.
2. NEET Study Material – To sincerely prepare for NEET we also help you with NEET study material both in Hard Copy and Soft Copy. Soft copy for NEET material is updated in your account immediately after the enrolment whereas we courier you the Hard Copy of NEET material at your home address in. This study material will be used for all the NEET online sessions and discussed accordingly.
3. NEET Online Test – NEET Online Test Series will be provided to the students. This NEET Test Series will be made available to the students in their account on the website. To keep you stay updated with your performance we conduct regular NEET Online Tests and based on the performance your class schedule is altered. So that we work on the weaker areas first.
4. NEET Doubt Removal Sessions – Special NEET doubt removal sessions are conducted every month where students can bring all their doubts for clarification by the faculty. These sessions are included and clubbed together in all NEET courses. With this, you don't have to run around to get an answer to the question or an explanation of a concept.
5. NEET Revision Notes – We have made sure that whatever you have learned in class, you should be able to take it back along with you. So, we provide you with the recordings of all these classes directly in your account. You can download your past class from your account and revise it as many times as you want.
NEET Courses Starting On:
NEET NRIs / OCIs & PIOs students who are planning to get admission in Medical Colleges in India through NEET can admission for NEET Coaching Classes on below-mentioned dates.
NEET Batches Starting:
| NEET Batches | Month (2018) | NEET Course Mode |
|---|---|---|
| NEET Prep – 1 Yr. & 2 Yr. | May – 18th & 23rd | Live & Interactive Online |
| NEET Prep – 1 Yr. & 2 Yr. | Jun – 6t & 15th | Live & Interactive Online |
| NEET Prep – 1 Yr. & 2 Yr. | Jul – 6t & 15th | Live & Interactive Online |
| NEET Prep – 1 Yr. & 2 Yr. | Aug – 6t & 15th | Live & Interactive Online |
| NEET Prep – 1 Yr. & 2 Yr. | Sep – 6t & 15th | Live & Interactive Online |
| NEET Prep – 1 Yr. & 2 Yr. | Oct- 6t & 15th | Live & Interactive Online |
| NEET Prep – 1 Yr. | Nov – 6t & 15th | Live & Interactive Online |
| NEET Prep – Crash Course | Dec – 6t & 15th | Live & Interactive Online |
| NEET Prep – Crash Course | Jan – 6t & 15th | Live & Interactive Online |
| NEET Prep – Crash Course | Feb – 6t & 15th | Live & Interactive Online |
NEET Faculties
All NEET aspirants want to study hard and ace the NEET test, we give our 100% but when it comes to the NEET faculty or NEET experts who are supposed to teach you further, is not qualified enough?
Having dealt with NRI students across the globe from major cities we found that students don’t have access to the required NEET teachers who are qualified to be a NEET Test Expert. Over a period of time student’s compromise with local tuition teachers or with school teachers, this results in achieving nothing.
When it comes to serious NEET medical preparation, you need
30+ Comments
0 Comments
- No comments available.












Post a Comment